Offensive Security for Small Business
Offensive security is a proactive approach that involves simulating real-world cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities, test defenses, and improve an organization’s security posture. By actively searching for weaknesses before malicious hackers do, businesses can stay ahead of evolving threats. Offensive security is especially important for identifying hidden gaps in systems, policies, and employee awareness.
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing)

- Objective: Identify and exploit security weaknesses to assess the effectiveness of current security measures.
- Benefits: Helps organizations discover unknown vulnerabilities, patch critical flaws, and comply with industry regulations (e.g., PCI-DSS, HIPAA).
Red Teaming

Red Teaming is a more advanced and comprehensive approach than traditional penetration testing. It simulates real-world, multi-faceted attacks over a longer period to test the organization’s entire security posture, including not just its technical defenses but also its people and processes. A “Red Team” acts like a sophisticated attacker, often using stealth techniques to evade detection while attempting to breach the organization’s defenses.
- Objective: Test the organization’s readiness against persistent and sophisticated cyberattacks by simulating complex, targeted attacks.
- Benefits: Red teaming challenges the effectiveness of the security measures and highlights weaknesses in incident response protocols and detection capabilities.
Vulnerability Assessment

Vulnerability Assessments involve scanning and analyzing an organization’s IT infrastructure to identify potential vulnerabilities. Unlike penetration testing, which actively attempts to exploit these weaknesses, vulnerability assessments focus on cataloging and prioritizing risks based on their potential impact.
- Objective: Provide a thorough overview of the vulnerabilities present in a system, including outdated software, misconfigurations, and unpatched security flaws.
- Benefits: Enables businesses to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, providing a roadmap for patching and improving security hygiene.
Social Engineering

- Objective: Test the organization’s ability to recognize and respond to deceptive tactics aimed at employees.
- Benefits: Helps companies improve employee awareness and resilience against real-life social engineering attacks, reducing the risk of human error leading to a breach.
Exploit Development
Exploit Development involves identifying vulnerabilities in software or systems and developing custom exploits to test the potential impact of those weaknesses. Offensive security teams use exploit development to simulate real-world attacks using both known vulnerabilities (those listed in public databases like CVEs) and unknown or “zero-day” vulnerabilities.
- Objective: Develop proof-of-concept attacks to demonstrate how vulnerabilities can be exploited and to provide insight into the potential damage of such an exploit.
- Benefits: Helps organizations understand the real-world impact of a security flaw and the urgency of fixing critical vulnerabilities.
Phishing Simulation

- Objective: Evaluate employee awareness and reactions to phishing attempts and educate them on how to spot and report suspicious emails.
- Benefits: Reduces the risk of a real phishing attack by improving employees’ ability to recognize and avoid phishing schemes, ultimately strengthening the organization’s human firewall.
Purple Teaming
Purple Teaming is the collaboration between the Red Team (offensive security experts) and the Blue Team (defensive security experts). This approach combines the strengths of both teams to test an organization’s defenses while simultaneously working to improve them. Red Teams simulate attacks, while Blue Teams defend against them, and the collaboration helps in identifying and patching gaps in real-time.
- Objective: Enhance the communication between offensive and defensive teams to ensure security improvements are immediate and effective.
- Benefits: Provides continuous feedback to strengthen defenses and helps organizations understand how well their defensive measures respond to real-world attacks.
Physical Security Testing

Physical Security Testing involves testing the physical defenses of an organization, such as locks, access control systems, and security personnel. Attackers may use physical breaches to gain unauthorized access to systems or sensitive areas, making it a crucial aspect of offensive security.
- Objective: Test the effectiveness of physical security measures to prevent unauthorized access to facilities or data centers.
- Benefits: Helps organizations understand how physical vulnerabilities, such as weak access control, can lead to digital compromises or data theft.
Application Security Testing

Application Security Testing focuses specifically on finding vulnerabilities in web or mobile applications. This includes testing for common flaws such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure APIs, and authentication issues.
- Objective: Identify and fix vulnerabilities in applications before they can be exploited in the wild.
- Benefits: Protects the organization’s customer-facing applications, reduces the risk of data breaches, and ensures compliance with security standards such as OWASP Top 10.
Threat Hunting

Threat Hunting is an active search for signs of malicious activity or potential threats that have bypassed existing security controls. While typically considered part of defensive security, it can be incorporated into offensive security strategies by identifying advanced threats that may have infiltrated the network unnoticed.
- Objective: Actively search for indicators of compromise (IoCs) and hidden threats within the network that traditional detection methods may miss.
- Benefits: Helps organizations detect and neutralize advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other sophisticated attacks that evade standard security tools.
Zero-Day Exploit Simulation

A Zero-Day Exploit Simulation involves mimicking attacks that exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities for which no official patch exists yet. Offensive security teams use these simulations to help organizations prepare for the unknown and unpatched flaws in software or hardware.
- Objective: Simulate attacks using vulnerabilities that are unknown or have not yet been publicly disclosed.
- Benefits: Helps companies build strategies for mitigating the impact of zero-day vulnerabilities, increasing resilience against new and evolving threats.
Attack Surface Management (ASM)
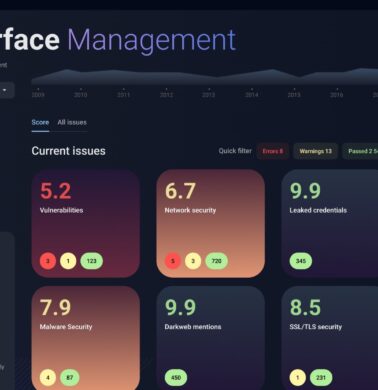
Attack Surface Management (ASM) involves continuously identifying and managing the potential entry points that attackers could exploit in an organization’s IT environment. This includes everything from publicly exposed IP addresses and web applications to shadow IT (unauthorized devices or applications).
- Objective: Continuously monitor and manage the organization’s attack surface to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Benefits: Reduces the risk of exposure from overlooked or misconfigured systems, helping organizations stay one step ahead of attackers.
Offensive security, including penetration testing, red teaming, vulnerability assessments, social engineering, exploit development, phishing simulations, and the additional techniques listed above, is essential for organizations to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities. By actively testing and improving their security posture, companies can better defend against both known and emerging cyber threats.
Incorporating offensive security practices empowers businesses to go beyond reactive defense measures, staying ahead of attackers and fortifying their cyber defenses in an increasingly complex threat landscape.